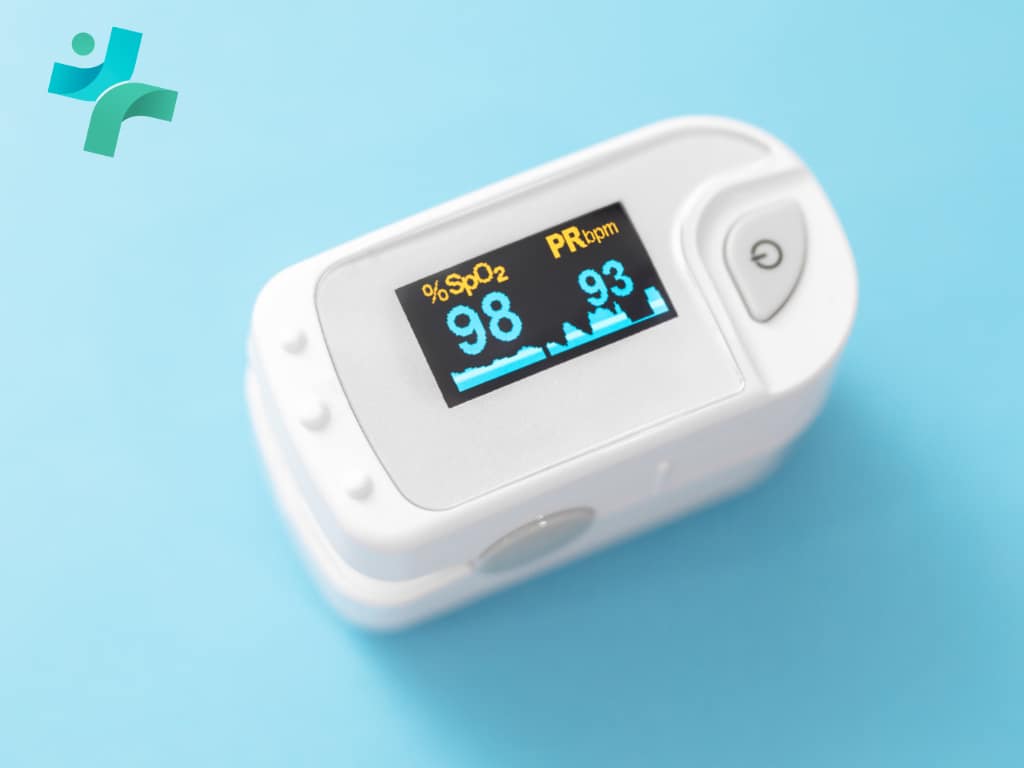
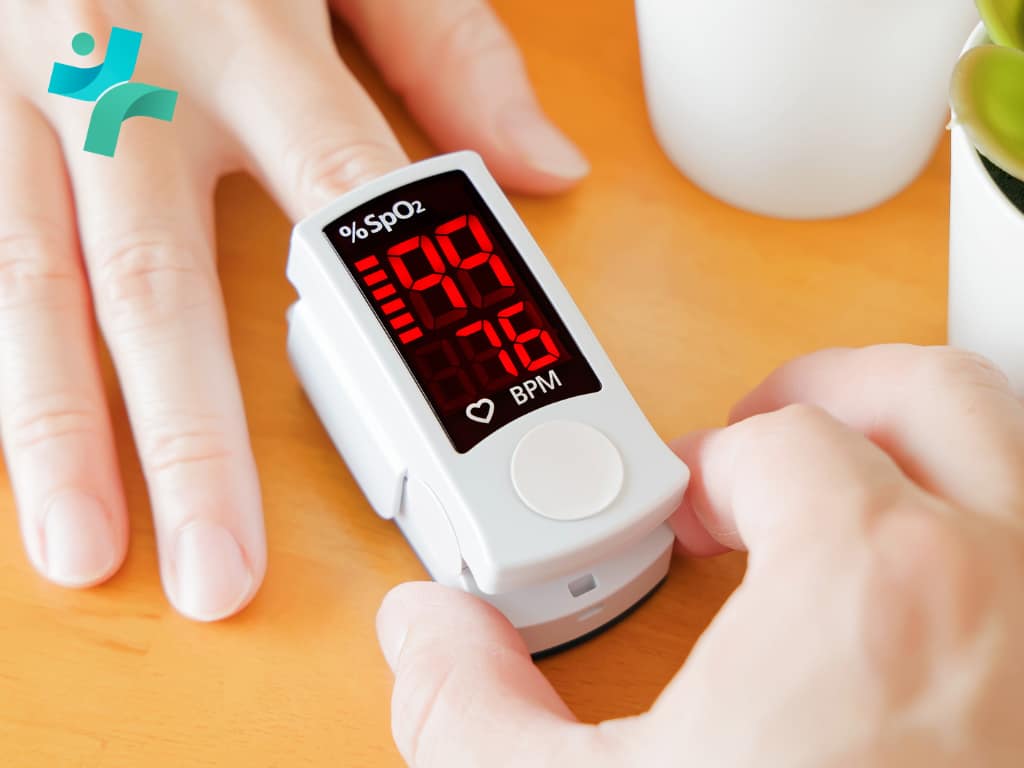
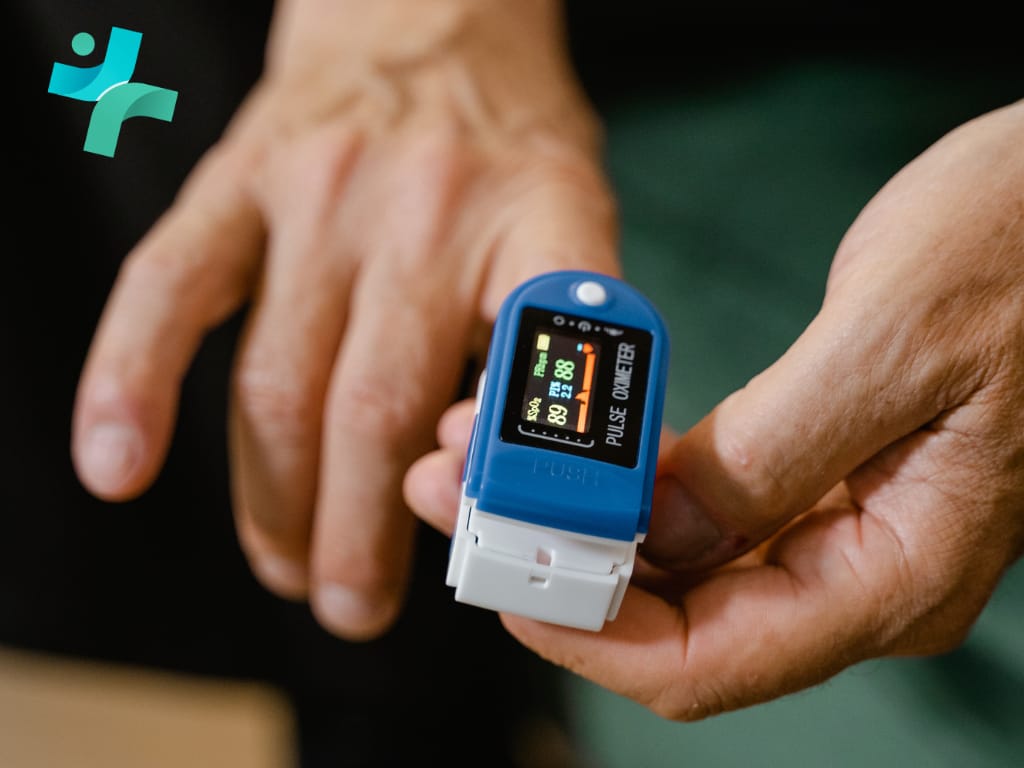
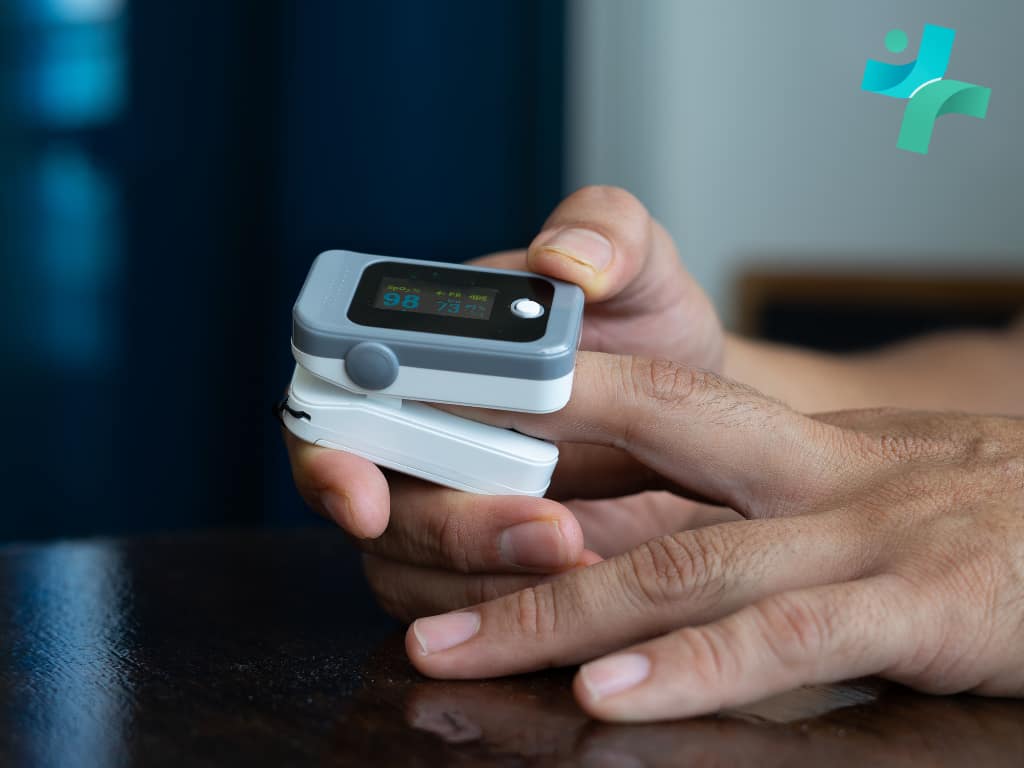
Pulse oximeter has revolutionized the way healthcare providers and patients manage chronic respiratory and cardiac conditions. This non-invasive tool measures the oxygen saturation level (SpO2) in the blood, providing immediate data on how well oxygen is being transported to the extremities furthest from the heart, including the legs and arms. Its simplicity, affordability, and effectiveness in delivering instant readings make pulse oximetry an indispensable part of chronic condition management.
Overview of Pulse Oximetry in Chronic Condition Management
Pulse oximeter is particularly beneficial in the management of chronic conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, heart failure, and others that affect the body’s ability to efficiently oxygenate the blood. By offering a quick and accurate assessment of a patient’s oxygenation status, pulse oximeters enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment plans, medication adjustments, and the need for supplemental oxygen, thereby preventing potential emergencies and hospitalizations.
Significance of Pulse Oximetry
Understanding the Importance of Regular Oxygen Saturation Monitoring
Maintaining optimal oxygen levels is crucial for patients with chronic conditions. Regular monitoring with a pulse oximeter can detect early signs of oxygen deprivation, which, if left unchecked, could lead to severe complications, including organ damage. For individuals managing chronic diseases, routine pulse oximetry readings can help track the effectiveness of treatment regimens and signal when adjustments are needed, ensuring that patients receive the right care at the right time.
Pulse Oximetry in Respiratory Conditions
Chronic respiratory conditions such as COPD and asthma significantly impact patients’ quality of life, often requiring continuous monitoring and management to maintain stable health.
Managing COPD with Pulse Oximetry
For patients with COPD, pulse oximetry provides vital data that can influence the course of treatment. Regular home monitoring allows for the detection of exacerbations early, enabling prompt intervention and adjustments to medication or oxygen therapy. This proactive approach helps in stabilizing the condition, reducing the risk of hospital admissions, and improving overall patient outcomes.
Asthma and Pulse Oximetry
Asthma control varies with environmental factors, allergen exposure, and individual health status. Pulse oximeters play a critical role in monitoring asthma, particularly during flare-ups or attacks. By measuring oxygen saturation levels, patients and caregivers can gauge the severity of an attack and decide on the immediacy of medical intervention. This monitoring is essential for preventing asthma-related complications and ensuring that patients maintain a normal, active lifestyle.
Pulse Oximetry in Cardiac Conditions
Cardiac conditions significantly affect the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, impacting oxygen distribution throughout the body. Pulse oximetry serves as a critical tool in managing these conditions by providing real-time data on oxygen saturation levels.
Heart Failure Management
In heart failure, the heart struggles to supply sufficient blood to meet the body’s needs, including oxygen delivery. Pulse oximetry monitoring enables healthcare providers to assess how well patients with heart failure are oxygenated. Regular use of pulse oximeters can help in identifying the need for supplemental oxygen or adjustments in medication. Moreover, it allows for the detection of acute events or deterioration in condition, necessitating immediate medical attention. By monitoring oxygen saturation, patients and clinicians can work together to manage heart failure more effectively, aiming to maintain stability and prevent complications.
Pulse Oximetry in Congenital Heart Diseases
Congenital heart diseases (CHD) present unique challenges in monitoring and management due to the structural abnormalities of the heart present from birth. Pulse oximetry plays a vital role in the early detection of hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels) in infants and children with CHD. Continuous or periodic monitoring can provide essential insights into the adequacy of oxygen circulation, which is crucial for the timely intervention and surgical planning. Moreover, pulse oximetry is used in long-term management and monitoring of CHD patients to ensure that their oxygen levels remain within a safe range as they grow.
Pulse Oximetry for Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete obstruction of the airway during sleep, leading to significant drops in oxygen levels.
The Importance of Overnight Monitoring
Overnight pulse oximetry monitoring is a non-invasive method to diagnose and manage OSA. By recording oxygen saturation levels throughout the night, it can identify patterns of significant oxygen desaturation that are indicative of sleep apnea episodes. This information is crucial for diagnosing OSA and determining its severity, guiding treatment decisions such as the need for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy or other interventions.
Interpreting Overnight Oximetry Results
Understanding the data from overnight oximetry involves looking for drops in oxygen levels that coincide with apnea events. A pattern of repetitive drops in oxygen saturation, typically by 3% or more, suggests the presence of OSA. Healthcare providers can use this data, along with other diagnostic information, to tailor treatment plans that address the specific needs of sleep apnea patients, enhancing their sleep quality and overall health.
Best Practices for Using Pulse Oximeters in Chronic Condition Management
Ensuring Accurate Readings
Accurate oximetry readings are essential for effective management of chronic conditions. Tips for obtaining reliable readings include:
- Ensuring the finger is warm, relaxed, and well-perfused before placing the oximeter.
- Avoiding nail polish or artificial nails that can interfere with the sensor.
- Keeping still during measurements to reduce the risk of inaccurate readings due to motion artifacts.
When to Report Changes
Patients and caregivers should be vigilant for significant changes in oxygen saturation levels. A consistent drop below 90% may indicate a need for medical evaluation and possible adjustment in treatment. It’s essential to communicate any concerning trends or readings with healthcare providers promptly to ensure timely interventions.
Future Perspectives
Advancements in Pulse Oximetry for Chronic Conditions
The landscape of pulse oximetry is on the brink of transformation, with emerging technologies promising to enhance the management of chronic conditions significantly. Innovations in sensor technology, wireless connectivity, and data analytics are expanding the capabilities of pulse oximeters, making them more accurate, user-friendly, and integrated with other health monitoring systems.
The Rise of Wearable Pulse Oximeters
One of the most exciting advancements is the development of wearable pulse oximeters, which allow for continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation levels without hindering the user’s daily activities. These devices can alert patients and healthcare providers to drops in oxygen levels in real-time, enabling prompt intervention even before symptoms worsen.
Furthermore, the integration of pulse oximetry data with electronic health records (EHRs) and telehealth platforms is improving the continuity of care. Patients can share their oximetry readings with their healthcare providers remotely, facilitating better monitoring of chronic conditions outside the clinical setting.
AI and ML: The Next Frontier in Oximetry
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are being applied to interpret oximetry data more effectively, identifying patterns and trends that may indicate the need for adjustments in treatment plans. This capability could lead to more personalized and proactive management of conditions such as COPD, asthma, and sleep apnea.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the potential to revolutionize how chronic conditions are monitored and managed, offering patients greater control over their health and well-being.
Conclusion
The advancements in pulse oximetry technology promise even greater improvements in patient care. With the advent of wearable devices, enhanced connectivity, and the application of AI and ML, pulse oximetry is set to become even more integral to chronic condition management. These innovations will not only enhance the accuracy and ease of monitoring but also empower patients with real-time insights into their health status, fostering a more proactive approach to managing their conditions.