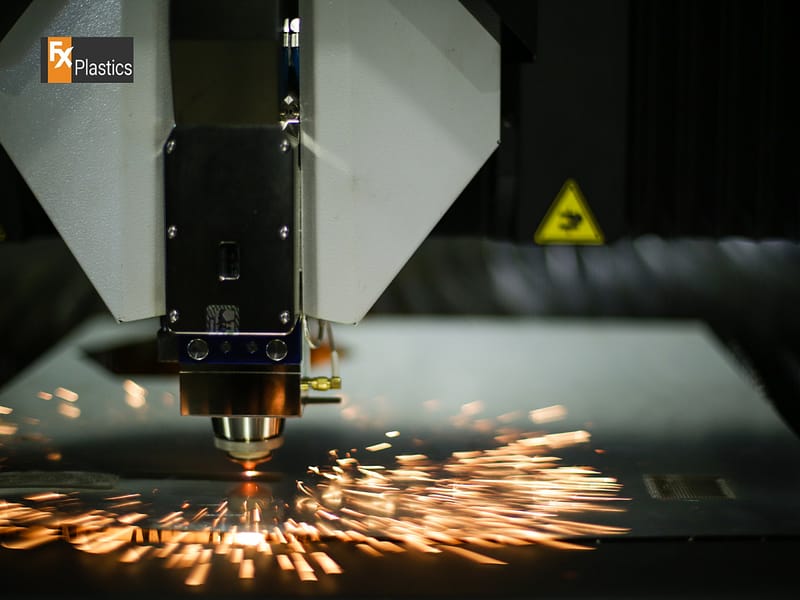
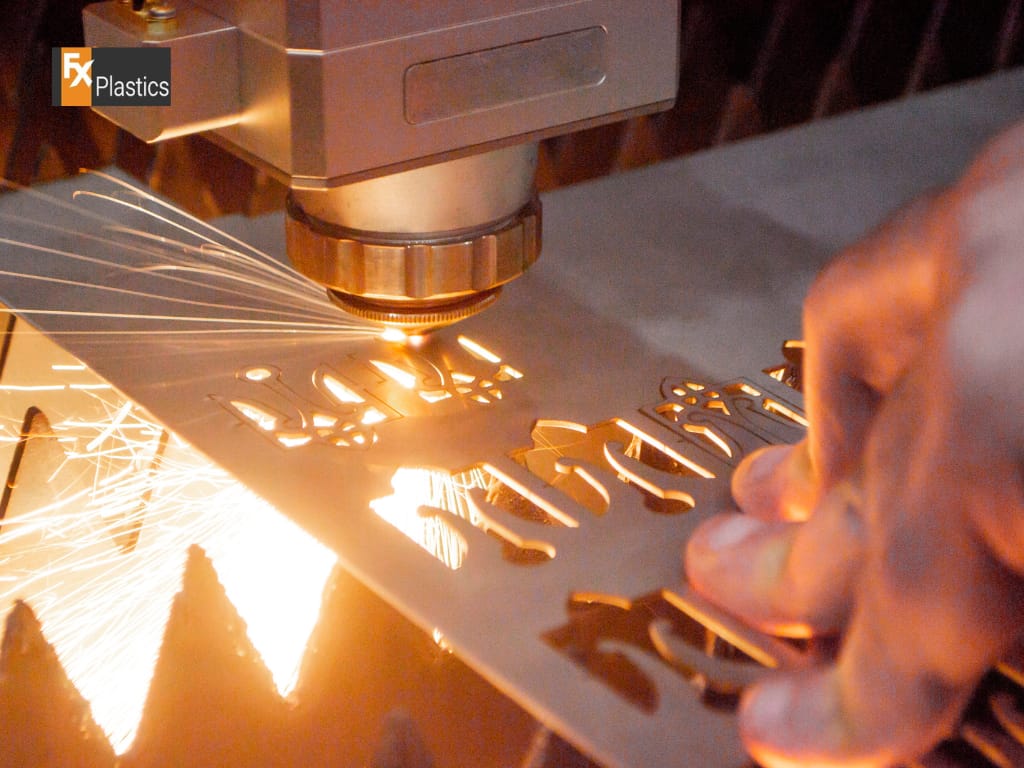
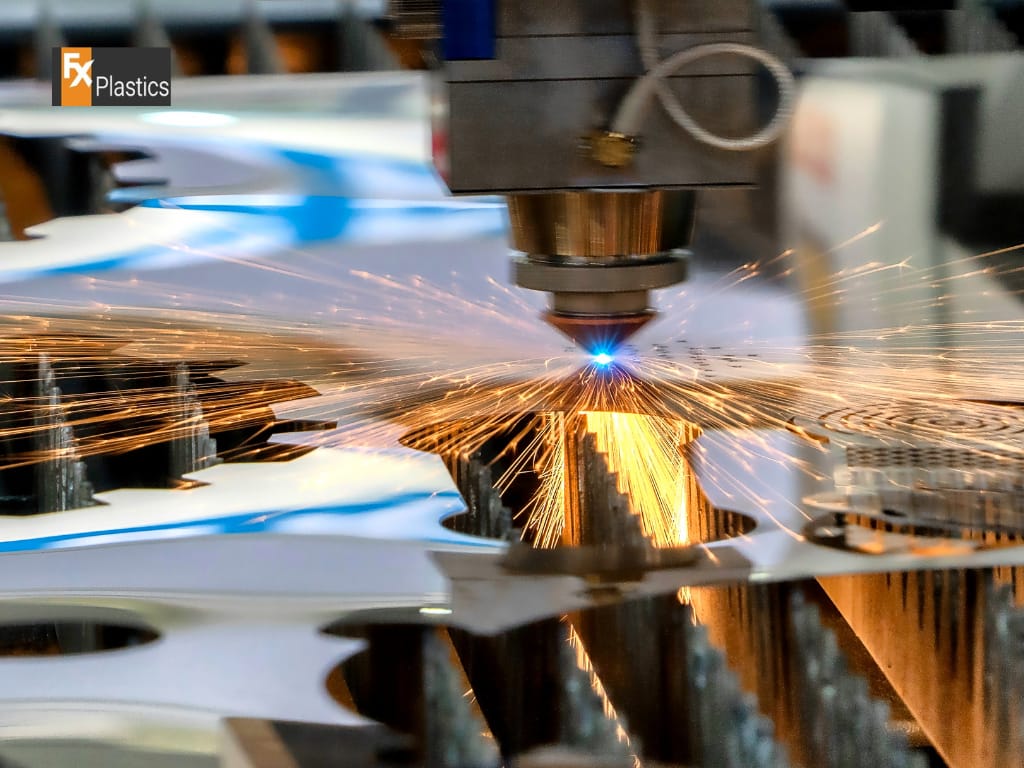
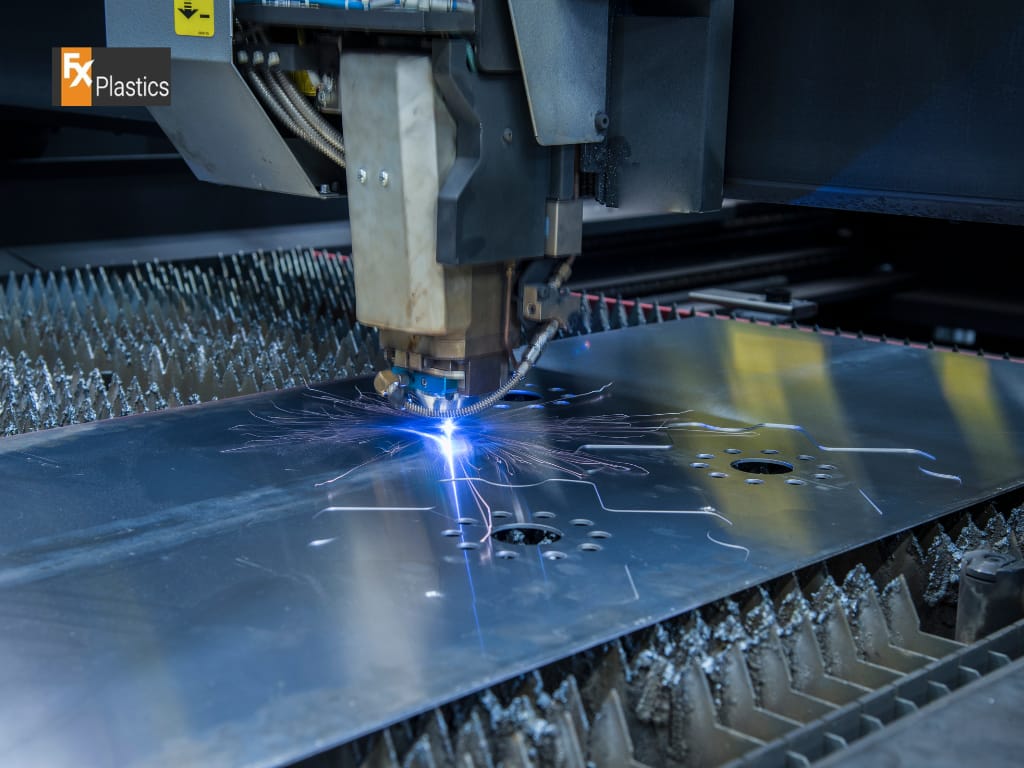
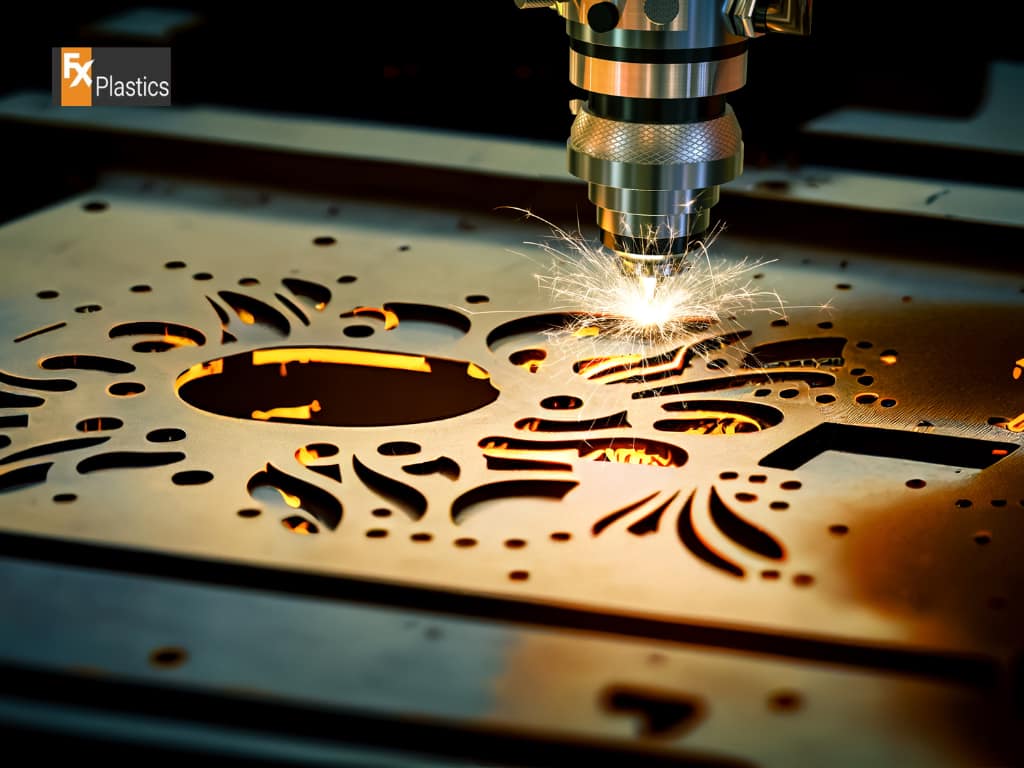
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) laser cutting is a pivotal technology in the realm of digital fabrication, offering precision cuts on a variety of materials, from metals to plastics and beyond. By directing a high-powered laser through optics, this method precisely cuts materials based on digital designs, making it indispensable for industries ranging from manufacturing to design. The choice of fabrication method is crucial for any project, as it directly impacts the final product’s quality, efficiency, and cost. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of CNC laser cutting, in comparison to other digital fabrication techniques, is essential for making informed decisions that align with project requirements, budget, and time constraints.
CNC Laser Cutting vs. 3D Printing
Overview of Both Methods
CNC laser cutting and 3D printing stand as pillars in digital fabrication, each with unique strengths. Laser cutting excels in slicing through materials with extreme precision by vaporizing areas with an intense laser beam. It’s ideal for two-dimensional cuts but can also achieve intricate designs with high accuracy. On the other hand, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer from digital models, offering unparalleled versatility in creating complex three-dimensional shapes.
Precision and Material Compatibility
The precision of CNC laser cutting is unmatched, capable of producing extremely detailed and accurate cuts with clean edges. It works well across a broad spectrum of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and glass. 3D printing, while also precise, has limitations based on the printing resolution and the material’s behavior during the printing process. It primarily handles plastics, resins, and metals (through specific methods like Direct Metal Laser Sintering), with ongoing advancements expanding its material range.
Speed and Cost-Effectiveness
CNC laser cutting is generally faster for producing flat components and can be more cost-effective for larger production runs. The speed of laser cutting allows for rapid turnaround times, especially when working with thin to medium-thickness materials. 3D printing is inherently slower due to its additive process, layering materials to create the final product, making it ideal for prototyping or small batches where complexity or customization is paramount.
CNC Laser Cutting vs. Waterjet Cutting
Key Differences
While CNC laser cutting uses a focused laser beam, waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive substance, to cut through materials. Waterjet cutting is renowned for its ability to slice through thicker materials than laser cutting can manage, including metals, stones, and composites, without introducing heat, thereby eliminating thermal distortion.
Material Limitations and Thickness
CNC laser cutting shines with materials like metals, plastics, and wood, particularly with thicknesses up to an inch for metals and several inches for softer materials. Waterjet cutting, however, can handle almost any material and thickness, offering more versatility for cutting thick metals and composite materials without the risk of heat-induced damage.
Finish Quality and Environmental Impact
Both methods produce high-quality finishes, with laser cutting providing slightly smoother edges on thinner materials. However, waterjet cutting avoids the potential for burnt edges or thermal stress. Environmentally, waterjet cutting has a lower carbon footprint as it doesn’t generate fumes or require as much energy as laser cutting. Both techniques, however, strive for sustainability through advancements in technology and operational efficiency.
CNC Laser Cutting vs. CNC Milling
Process and Application
CNC milling and CNC laser cutting are both stalwarts in the manufacturing industry, each with unique benefits depending on the application. CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses rotating multipoint cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, making it ideal for creating complex three-dimensional shapes and components. It’s particularly suited for projects requiring deep cuts and the production of parts like gears, threads, and slots in metals, plastics, and wood.
CNC laser cutting, in contrast, directs a high-powered laser through optics to cut materials with precision. This method is renowned for its accuracy and speed in producing flat, two-dimensional shapes. It excels in applications where intricate designs and tight tolerances are necessary, particularly in sheet metal fabrication, intricate woodworking, and cutting of delicate materials like fabrics and thin plastics.
Material Removal and Efficiency
CNC milling is inherently a subtractive process, removing material to shape the final product. This method can be less material-efficient than laser cutting, as it produces more waste. However, milling offers unparalleled versatility in working with a diverse range of materials, including very hard metals, and in executing deep cuts and complex geometries.
Laser cutting is characterized by its precision and efficiency, especially suited for cutting thin to medium-thickness materials. It minimizes material waste by making precise cuts and is generally faster than milling when creating parts with simpler, flatter geometries.
Detail and Versatility
Both methods achieve a high level of detail, though their applications differ. CNC milling can create highly detailed three-dimensional pieces with precise depths and angles, accommodating a wide variety of designs. Its versatility in handling a broad spectrum of materials and geometries makes it a go-to for intricate, custom parts.
CNC laser cutting stands out for its ability to produce extremely precise and detailed two-dimensional cuts. Its versatility shines in the range of materials it can process and the intricate patterns and designs it can achieve, especially on flat surfaces.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Fabrication Method
Project Requirements
The choice between CNC laser cutting and milling largely depends on the specific needs of the project. Considerations include:
- Material Type and Thickness: Some materials may be better suited to one method over the other.
- Desired Finish: Each method offers different finishes, affecting the appearance and functionality of the final piece.
Budget and Time Constraints
Cost and production time are critical factors in deciding between laser cutting and milling. While laser cutting may offer quicker turnaround times for simpler designs, CNC milling might provide a more cost-effective solution for producing complex parts in lower volumes.
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is an increasingly important factor in manufacturing decisions. Laser cutting is generally considered to have a lower environmental impact due to its precision and material efficiency, though advancements in CNC milling technology are continually reducing its ecological footprint.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between CNC laser cutting and CNC milling is vital for selecting the most appropriate digital fabrication technique for your project. Each method has its strengths, suited to different types of materials, designs, and applications. By carefully considering the project requirements, budget, time constraints, and environmental impact, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your objectives. Always consider consulting with fabrication experts who can offer insights based on experience with various materials and projects. Embracing the right fabrication method opens up possibilities for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in your projects.